https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1kbPohN59t4&t=37s
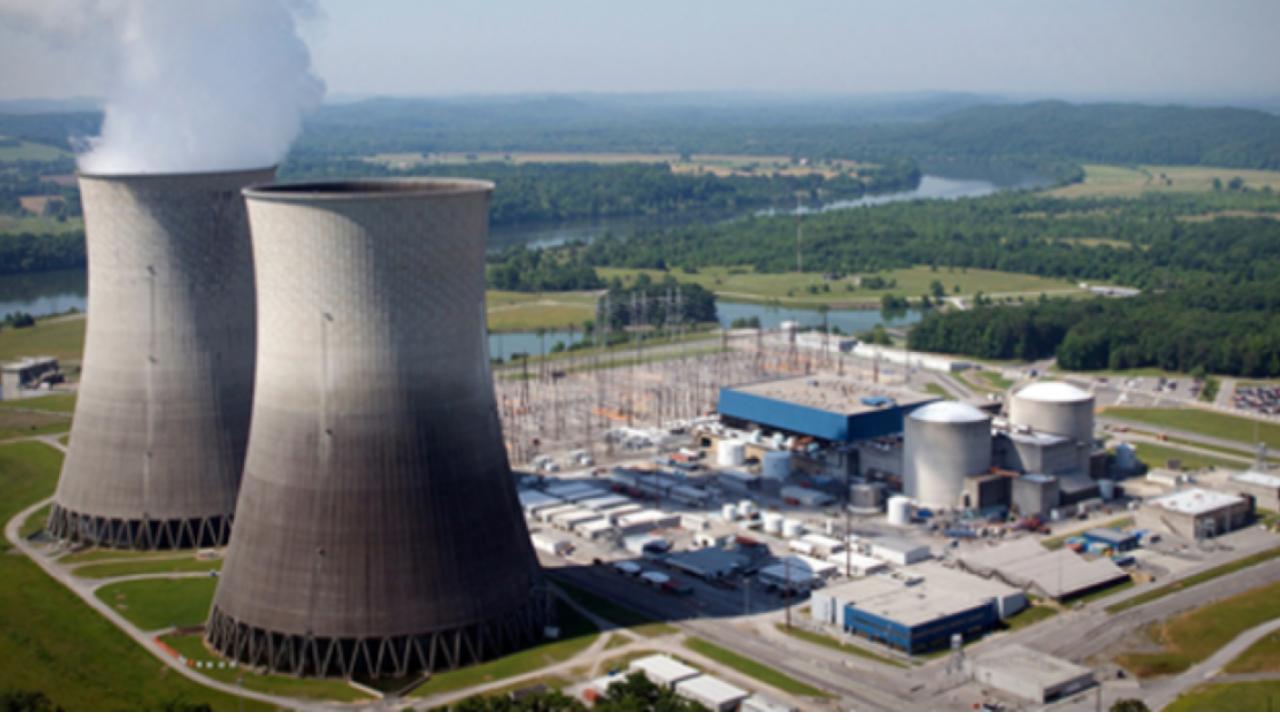
Nuclear energy is produced by splitting atoms apart through a physical process called fission.
The main job of a reactor is to house and control fisison.
Reactors use uranium for nuclear fuel.
The uranium is processed into small ceramic pellets and stacked together into sealed metal tubes called fuel rods.
Inside the reactor vessel, the fuel rods are immersed in water which acts as both a coolant and moderator.
The moderator helps slow down the neutrons produced by fission to sustain the chain reaction.
Control rods can then be inserted into the reactor core to reduce the reaction rate or withdrawn to increase it.
The heat created by fission turns the water into steam, which spins a turbine to produce carbon-free electricity.