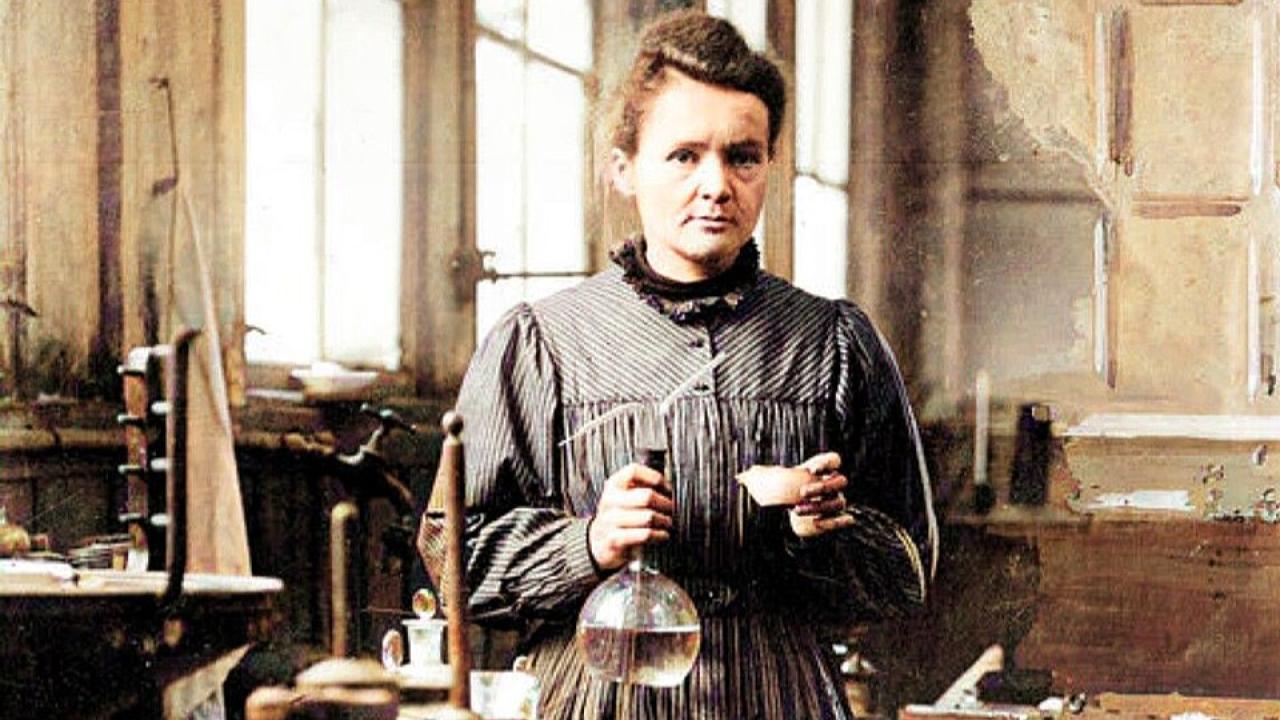
Women have significantly contributed to science throughout history, though often underrecognized. From Marie Curie’s groundbreaking work in radioactivity to Rachel Carson’s environmental activism, women have made profound impacts in various scientific fields.
However, systemic barriers and underrepresentation have historically limited their participation and recognition. Despite these challenges, efforts to promote gender equality in science continue, with initiatives like the International Day of Women and Girls in Science and organizations like L’Oréal-UNESCO For Women in Science working to empower women in STEM.